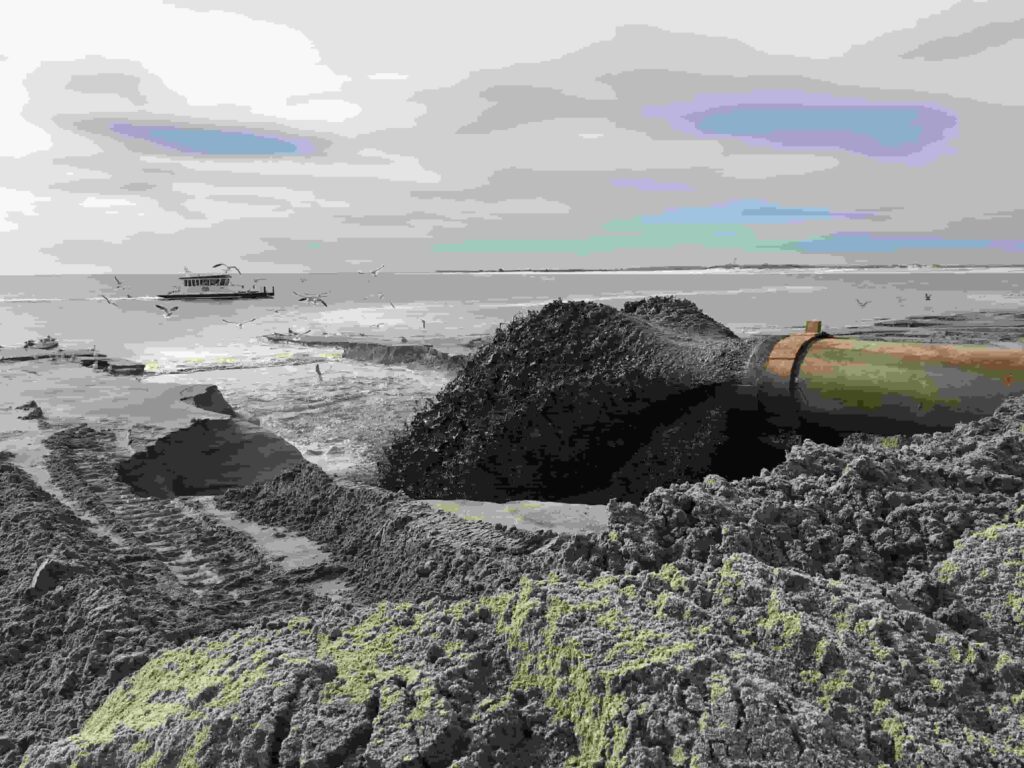
Dredging the Sea
Dredging involves the excavation and removal of sediments, debris, or materials from the bottom of a body of water such as seas, rivers, or harbors. This process is often undertaken to deepen waterways, maintain navigational channels, and create space for ports or coastal development. Dredging can also help prevent flooding by improving water flow and clearing blockages.
While dredging supports infrastructure development and economic activities, it can also have environmental impacts, such as habitat disruption, sediment release, and potential pollution. Therefore, careful planning and sustainable practices are essential to balance its benefits with ecological preservation.
Why We Dredge
Dredging is essential for various practical, economic, and environmental reasons, including:
- Maintaining Navigation:
- To ensure ships, boats, and other vessels can navigate safely in ports, harbors, and waterways by removing accumulated silt and debris.
- Coastal Development:
- To create or expand areas for infrastructure like ports, marinas, or land reclamation projects.
- Flood Control:
- To enhance water flow in rivers and drainage systems, reducing the risk of flooding during heavy rains or high tides.
- Environmental Restoration:
- To remove contaminated sediments or restore natural habitats such as wetlands and aquatic ecosystems.
- Mining and Resource Extraction:
- To extract valuable materials like sand, gravel, or minerals from the seabed.
- Improving Water Quality:
- To remove pollutants and excessive organic matter, promoting healthier aquatic environments.
Dredging is a critical activity in supporting modern infrastructure and environmental management, though it requires careful regulation to minimize ecological impacts.